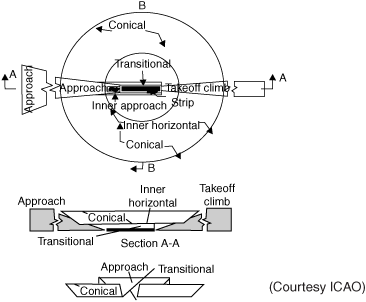
obstacle-limitation surfaces
- obstacle-limitation surfaces
The outer-horizontal, conical, inner-horizontal, approach, inner-approach, transitional, inner-transitional, balked-landing, and takeoff climb surfaces make up the obstacle-limitation surfaces. The outer-horizontal surface is a plane located 500 ft (150 m) above the established airfield elevation, extending outward from the outer periphery of the conical surface for a distance of 30,000 ft (9000 m). The conical surface extends from the periphery of the inner-horizontal surface outward and upward at a slope of 20 to 1 for a horizontal distance of 7000 ft (2100 m) to a height of 500 ft (150 m) above the established airfield elevation. The inner-horizontal surface is a plane that is oval in shape at a height of 150 ft (50 m) above the established airfield elevation. The plane is constructed by scribing an arc with a radius of 7500 ft (2250 m) about the centerline at the end of each runway and interconnecting these with arcs at the tangents. The approach surface is an inclined plane or combination of planes preceding the threshold. The inner-approach surface is a rectangular portion of the approach surface immediately preceding the threshold. The transitional surfaces connect the primary surfaces, the first 200 ft (60 m) of the clear zone surfaces, and the approach clearance surfaces to the inner-horizontal surface, conical surface, outer-horizontal surface, or other transitional surfaces. The slope of the transitional surface is 7 (horizontal) to 1 (vertical) outward and upward at right angles to the runway centerline. The inner-transitional surface is similar to the transitional surface but closer to the runway. The balked-landing surface is an inclined plane located at a specified distance after the threshold, extending between the inner- and outer-transitional surfaces. The takeoff climb surface is an inclined plane or another specified surface beyond the end of the runway or clearway.
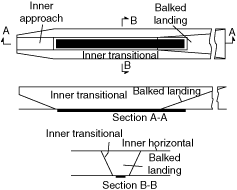
Inner approach, inner transitional, and balked landing obstacle limitation surface.
Aviation dictionary.
2014.
Look at other dictionaries:
obstacle-free zone — The obstacle free zone is a three dimensional volume of airspace set up to protect aircraft transitioning to and from the runway. The OFZ clearing standard precludes taxiing and parked airplanes and object penetrations, except for frangible… … Aviation dictionary
Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport — Bombay Airport, Mumbai Airport and Sahar Airport redirect here. For Mumbai s general aviation airport, see Juhu Aerodrome. Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport छ्त्रपती शिवाजी आंतरराष्ट्रीय विमानतळ … Wikipedia
PANS-OPS — (Procedures for Air Navigation Services Aircraft Operations) is an ATC term denominating rules for designing instrument approach and departure procedures. Such procedures are used to allow aircraft to land and take off under Instrument… … Wikipedia
ALGÉRIE — En 1962, les fées ont été particulièrement nombreuses à se presser autour de l’Algérie. L’« exemplarité » de la lutte de libération nationale, longue et violente, ravissait ceux qui ne voient de progrès humain que dans l’action de l’« accoucheuse … Encyclopédie Universelle
AÉRODYNAMIQUE — L’aérodynamique, dont l’étymologie évoque immédiatement l’action de l’air en mouvement, est la science qui étudie les différents aspects de cette action, notamment les forces, pressions et moments qui résultent du déplacement des corps dans… … Encyclopédie Universelle
POLLUTION — Bien que d’usage banal à l’heure actuelle, le terme de pollution recouvre des acceptions fort diverses et qualifie une multitude d’actions qui dégradent d’une façon ou d’une autre le milieu naturel. Certes, le vocable désigne sans ambiguïté les… … Encyclopédie Universelle
THERMIQUE — La thermique est la branche de la physique qui traite des échanges de chaleur accompagnés ou non d’échange de masse et de changement de phases. Elle peut donc être considérée comme partie intégrante de la thermodynamique des phénomènes… … Encyclopédie Universelle
Foil — Plan porteur (mécanique des fluides) En mécanique des fluides, un plan porteur est une surface portante qui se déplace dans un fluide. Sommaire 1 Application aux navires 2 Principaux types de plans porteurs hydrodynamiques 2.1 Plan porteurs de… … Wikipédia en Français
Plan porteur (mecanique des fluides) — Plan porteur (mécanique des fluides) En mécanique des fluides, un plan porteur est une surface portante qui se déplace dans un fluide. Sommaire 1 Application aux navires 2 Principaux types de plans porteurs hydrodynamiques 2.1 Plan porteurs de… … Wikipédia en Français
Plan porteur (mécanique des fluides) — En mécanique des fluides, un plan porteur est une surface qui se déplace dans un fluide et transmet une force à son support. Hydrofoil Aldebaran Sommaire 1 Applic … Wikipédia en Français
 Inner approach, inner transitional, and balked landing obstacle limitation surface.
Inner approach, inner transitional, and balked landing obstacle limitation surface.